排序
iOS 中的几种排序方法.
准备工作
NSArray *data = [NSArray arrayWithObjects:
@"12",@"4",@"3",@"10",@"25",
@"17",@"22",@"44",@"1",@"18",
@"35",@"11",@"21",@"16",@"34",
@"63",@"102",@"65",@"37",@"97", nil];
NSArray *resaultArr;
// 计算代码运行时间
CFAbsoluteTime startTime = CFAbsoluteTimeGetCurrent();
resaultArr = [self bubbleSort:data];
CFAbsoluteTime linkTime = (CFAbsoluteTimeGetCurrent() - startTime);
NSLog(@"冒泡排序 Linked in %f ms", linkTime * 1000.0);
// NSLog(@"%@",resaultArr);
startTime = CFAbsoluteTimeGetCurrent();
resaultArr = [self selectSort:data];
linkTime = (CFAbsoluteTimeGetCurrent() - startTime);
NSLog(@"选择排序 Linked in %f ms", linkTime * 1000.0);
// NSLog(@"%@",resaultArr);
startTime = CFAbsoluteTimeGetCurrent();
resaultArr = [self hillSort:data];
linkTime = (CFAbsoluteTimeGetCurrent() - startTime);
NSLog(@"希尔排序 Linked in %f ms", linkTime * 1000.0);
// NSLog(@"%@",resaultArr);
startTime = CFAbsoluteTimeGetCurrent();
resaultArr = [self quicksort:data];
linkTime = (CFAbsoluteTimeGetCurrent() - startTime);
NSLog(@"快速排序 Linked in %f ms", linkTime * 1000.0);
// NSLog(@"%@",resaultArr);
冒泡排序
/**
冒泡排序
@param dataSourceArr 数据源
@return 有序数据
*/
- (NSArray *)bubbleSort:(NSArray *)dataSourceArr {
NSMutableArray *currentArray = dataSourceArr.mutableCopy;
NSInteger count = dataSourceArr.count;
//外循环控制 多少轮
for (NSInteger i = 0; i < count; i++) {
//内循环比较 j元素 跟 j+1 比较 相邻的元素
for (NSInteger j = 0; j < count - 1 - i; j++) {
if ([currentArray[j] integerValue] > [currentArray[j + 1] integerValue]) {
NSObject *temp = currentArray[j + 1];
currentArray[j + 1] = currentArray[j];
currentArray[j] = temp;
}
}
}
return currentArray.copy;
}
选择排序
/**
选择排序
@param dataSourceArr 数据源
@return 有序数据
*/
- (NSArray *)selectSort:(NSArray *)dataSourceArr {
NSMutableArray *currentArray = dataSourceArr.mutableCopy;
NSInteger count = dataSourceArr.count;
//外层控制轮数 需要比较多少轮
for (NSInteger i = 0; i < count; i++) {
//每轮跟其它元素比较 选出最大的 交换
for (NSInteger j = i + 1; j < count; j++) {
if ([currentArray[i] integerValue] > [currentArray[j] integerValue]) {
NSObject *temp = currentArray[j];
currentArray[j] = currentArray[i];
currentArray[i] = temp;
}
}
}
return currentArray.copy;
}
希尔排序
示意图
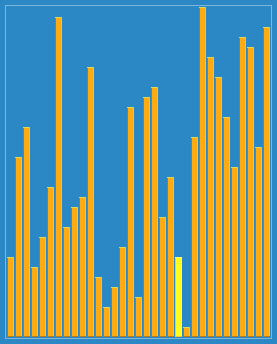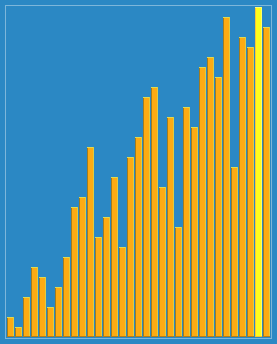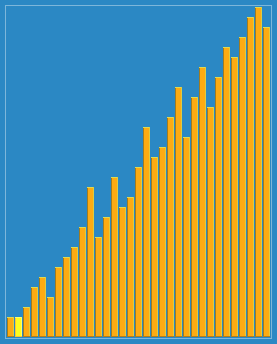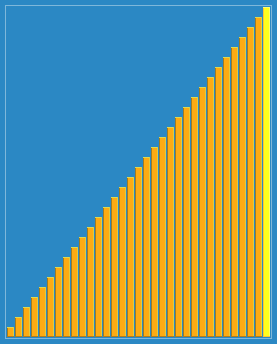
/**
希尔排序
@param dataSourceArr 数据源
@return 有序数组
*/
- (NSArray *)hillSort:(NSArray *)dataSourceArr {
/*
步长的选择是希尔排序的重要部分。只要最终步长为1任何步长序列都可以工作。算法最开始以一定的步长进行排序。然后会继续以一定步长进行排序,最终算法以步长为1进行排序。当步长为1时,算法变为插入排序,这就保证了数据一定会被排序。
已知的最好步长序列是由Sedgewick提出的(1, 5, 19, 41, 109,...),该序列的项来自 {\displaystyle 9\times 4^{i}-9\times 2^{i}+1} 9\times 4^{i}-9\times 2^{i}+1和 {\displaystyle 2^{i+2}\times (2^{i+2}-3)+1} 2^{{i+2}}\times (2^{{i+2}}-3)+1这两个算式。这项研究也表明“比较在希尔排序中是最主要的操作,而不是交换。”用这样步长序列的希尔排序比插入排序要快,甚至在小数组中比快速排序和堆排序还快,但是在涉及大量数据时希尔排序还是比快速排序慢。
另一个在大数组中表现优异的步长序列是(斐波那契数列除去0和1将剩余的数以黄金分区比的两倍的幂进行运算得到的数列):(1, 9, 34, 182, 836, 4025, 19001, 90358, 428481, 2034035, 9651787, 45806244, 217378076, 1031612713,…)
*/
NSMutableArray *currentArray = dataSourceArr.mutableCopy;
NSInteger gap = currentArray.count / 2;
NSInteger i,j;
while (gap >= 1) {
for (i = gap; i < currentArray.count; i ++) {
NSString *temp = currentArray[i];
for (j = i - gap; j >= 0 && [currentArray[j] integerValue] > [temp integerValue]; j -= gap)
currentArray[j + gap] = currentArray[j];
currentArray[j + gap] = temp;
}
gap = gap / 2;
}
return currentArray.copy;
}
// OpenAI 的答案 。。。。。。
func shellSort<T: Comparable>(_ array: [T]) -> [T] {
var a = array
let n = a.count
var gap = n / 2
while gap > 0 {
for i in gap..<n {
let temp = a[i]
var j = i
while j >= gap && a[j - gap] > temp {
a[j] = a[j - gap]
j -= gap
}
a[j] = temp
}
gap /= 2
}
return a
}
快速排序
示意图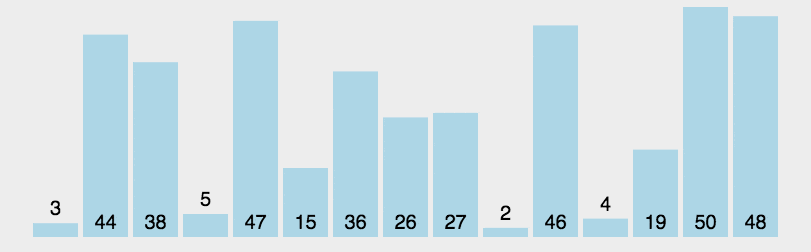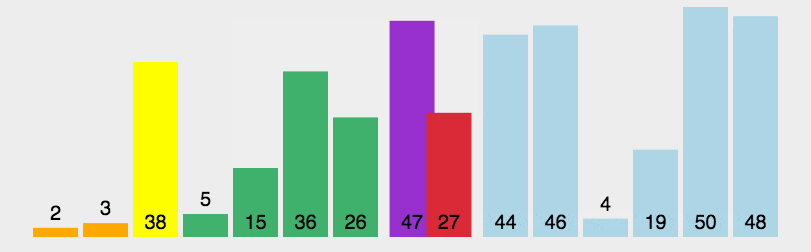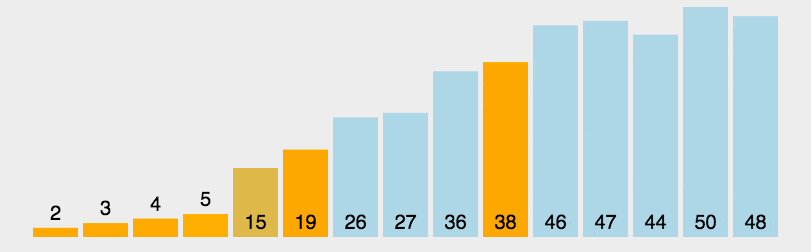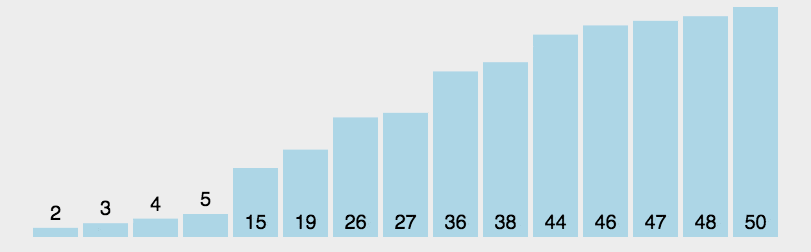
/**
快速排序
@param dataSourceArr 数据源
@return 有序数据
*/
- (NSArray *)quicksort:(NSArray *)dataSourceArr {
NSMutableArray *currentArray = dataSourceArr.mutableCopy;
NSInteger i,j,key;
for (i = 1; i < [currentArray count]; i++) {
key = [currentArray[i] integerValue];
j = i-1;
while ((j >= 0) && ([currentArray[j] integerValue] > key)) {
currentArray[j+1] = currentArray[j];
j--;
}
currentArray[j+1] = @(key);
}
return currentArray.copy;
}
函数用时

结语
希尔排序比冒泡排序和选择排序要快很多! 快排果然快!🤣